What are the functions of RBI (Reserve Bank of India)?
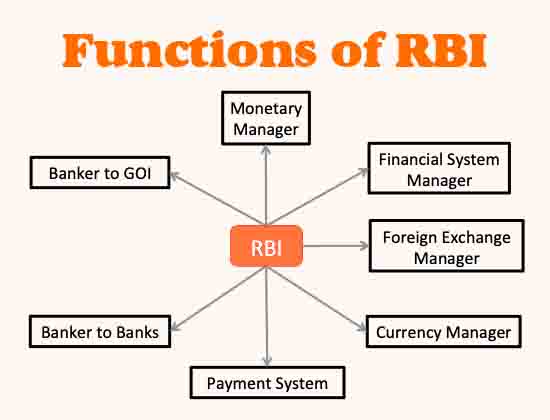
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India’s central bank, established in 1935. It is responsible for regulating the country’s monetary policy, managing foreign exchange reserves, and supervising the banking system. In this article, we will explore the functions of RBI and how it impacts India’s economy.
Regulating Monetary Policy
One of the primary functions of RBI is to regulate the country’s monetary policy. This involves controlling the supply and demand of money in the economy through various tools such as interest rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations. RBI’s monetary policy aims to maintain price stability, promote economic growth, and manage inflation.
Managing Foreign Exchange Reserves
RBI is responsible for managing India’s foreign exchange reserves, which are used to stabilize the value of the Indian rupee against other major currencies. These reserves are used to intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent excessive volatility in the exchange rate. The RBI also manages the country’s balance of payments by regulating the inflow and outflow of foreign exchange.
Supervising the Banking System
RBI is responsible for supervising and regulating the banking system in India. This includes issuing licenses to banks, setting prudential norms for banks, and monitoring their performance. RBI also acts as a lender of last resort, providing emergency funding to banks during times of financial stress.
Issuing Currency
RBI is responsible for issuing currency notes and coins in India. It manages the supply of currency to meet the demand of the economy and ensures that there is enough cash in circulation to facilitate transactions. RBI also manages the process of demonetization, which involves withdrawing certain currency notes from circulation and replacing them with new ones.
Promoting Financial Inclusion
RBI is committed to promoting financial inclusion in India. This involves providing banking services to underprivileged sections of society, such as rural populations and low-income households. RBI has introduced various measures to promote financial inclusion, such as allowing banks to open no-frills accounts and setting up a financial inclusion fund.
Related Articles –
Conducting Research and Analysis
RBI conducts research and analysis on various economic and financial issues in India. This includes monitoring macroeconomic indicators such as GDP, inflation, and employment, as well as conducting surveys and studies on specific topics such as digital payments and financial literacy. This research helps RBI to formulate policies and make informed decisions that benefit the economy.
Conclusion
The Reserve Bank of India plays a crucial role in India’s economy by regulating monetary policy, managing foreign exchange reserves, supervising the banking system, issuing currency, promoting financial inclusion, and conducting research and analysis. By performing these functions effectively, RBI helps to promote economic growth, stability, and financial inclusion in India.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is RBI?
A: RBI stands for Reserve Bank of India, which is the central bank of India. It was established on April 1, 1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Q: What are the functions of RBI?
A: RBI has several functions, including:
Monetary policy: RBI formulates and implements monetary policy to maintain price stability and promote economic growth.
Regulation and supervision of financial institutions: RBI regulates and supervises banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions to ensure their safety and soundness.
Issuance and management of currency: RBI is responsible for the issuance and management of currency in India.
Management of foreign exchange: RBI manages India’s foreign exchange reserves and oversees foreign exchange transactions.
Development of the financial system: RBI promotes the development of the financial system in India by introducing new financial instruments, setting up payment systems, and conducting research.Q: Why is RBI important?
A: RBI plays a critical role in the Indian economy. Its functions help to ensure the stability and efficiency of the financial system, maintain price stability, and promote economic growth.
Q: What is RBI’s role in regulating banks?
A: RBI is responsible for regulating and supervising banks in India. It issues licenses to new banks, sets prudential norms for banks’ capital adequacy, asset quality, and liquidity, and monitors their compliance with these norms. RBI also conducts inspections of banks to assess their financial health and takes corrective action if necessary.
Q: What is RBI’s role in monetary policy?
A: RBI formulates and implements monetary policy to maintain price stability and promote economic growth. It uses a range of tools, such as the repo rate, reverse repo rate, and cash reserve ratio (CRR), to influence the supply of money and credit in the economy.
Q: How does RBI manage India’s foreign exchange reserves?
A: RBI manages India’s foreign exchange reserves by buying and selling foreign currencies in the foreign exchange market. It also invests these reserves in safe and liquid assets, such as US Treasury bonds and other sovereign bonds.
Q: What is RBI’s role in promoting financial inclusion?
A: RBI promotes financial inclusion by encouraging banks to reach out to underserved and unbanked areas of the country. It has introduced several measures, such as priority sector lending and the Jan Dhan Yojana, to promote financial inclusion and provide banking services to all segments of society.

[…] main participants in the Indian foreign exchange market are the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), corporate entities, and individuals. The RBI […]
[…] not hold a banking license. NBFCs are registered under the Companies Act, 2013 and regulated by the Reserve Bank of India […]