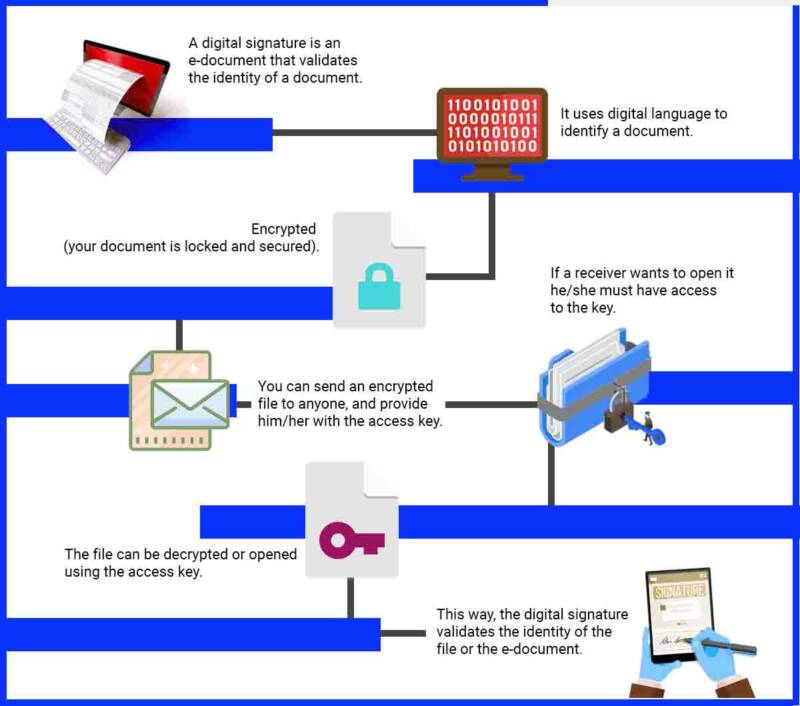
In today’s world, where digital communication and transactions have become a part of our daily lives, security is of paramount importance. Digital signatures play a significant role in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital documents and transactions. In this article, we will delve into what a digital signature is and how it works.
A digital signature is an electronic method used to authenticate the identity of the sender of a message or the signer of a document, and to ensure that the content of the message or document has not been tampered with during transmission. It is a mathematical algorithm that is applied to the digital data to create a unique digital fingerprint, which can be used to verify the authenticity of the message or document.
A digital signature is created using a combination of public-key cryptography and hash functions. Public-key cryptography involves the use of a pair of keys, a public key and a private key. The private key is kept secret by the owner, while the public key is available to anyone who wants to verify the authenticity of the signature.
To create a digital signature, the sender first creates a message or document and then generates a hash of the message using a cryptographic hash function. The hash is a unique and fixed-length string of characters that is derived from the content of the message.
The sender then encrypts the hash using their private key, creating the digital signature. The signature is then attached to the message or document, along with the sender’s public key.
When the recipient receives the message or document, they use the sender’s public key to decrypt the digital signature, revealing the hash of the original message. They then generate a new hash of the message using the same cryptographic hash function, and compare it to the hash that was decrypted from the digital signature. If the two hashes match, then the message or document has not been tampered with during transmission, and the sender’s identity has been authenticated.
Digital signatures provide a secure and efficient method for verifying the authenticity of digital documents and transactions. They can be used to sign contracts, financial transactions, legal documents, and other important digital records. Digital signatures are legally binding in many countries and are accepted as evidence in courts of law.
Digital signatures are an essential tool for ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital documents and transactions. By combining public-key cryptography and hash functions, digital signatures provide a secure and efficient method for verifying the identity of the sender and ensuring that the content of the message or document has not been tampered with during transmission. With the increasing use of digital communication and transactions, digital signatures have become an indispensable tool for ensuring trust and security in the digital world.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
A: A digital signature is an electronic method of authenticating the identity of a person or entity who signs a document or message. It is used to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of electronic documents.
A: A digital signature works by using a mathematical algorithm to encrypt a digital document or message. The digital signature algorithm generates a unique signature for the document that can be verified by the recipient. The signature ensures that the document has not been tampered with and that the sender is who they claim to be.
A: A digital signature consists of three components: the original electronic document, a digital signature algorithm, and a digital signature certificate.
A: A digital signature algorithm is a mathematical formula used to create a digital signature. It uses a combination of a private key and a public key to encrypt the document or message.
A: A digital signature certificate is an electronic document that contains information about the signer, including their name, address, and public key. It is issued by a trusted third party, known as a certification authority (CA).
A: The certification authority (CA) is responsible for verifying the identity of the signer and issuing a digital signature certificate. The CA acts as a trusted third party that vouches for the authenticity of the digital signature.
A: A properly implemented digital signature is very difficult to forge or tamper with. Any attempt to alter the document or signature will be detected during the verification process.
A: Digital signatures are used in a variety of applications, including electronic contracts, online transactions, and e-government services. They are also used to sign and encrypt emails and other digital documents.
A: Yes, a digital signature is legally binding in most countries, including the United States, European Union, and India. It is recognized as equivalent to a handwritten signature in electronic transactions.
This post was last modified on %s = human-readable time difference 2:00 pm
आज के डिजिटल युग में, छोटी-मोटी हिसाब-किताब का काम हमारे हर रोज के काम का हिस्सा बन चुका है। चाहे…
सुकन्या योजना में 14 वर्ष तक ₹250 जमा करेंगे तो 18 वर्ष में कितना मिलेगा? सुकन्या समृद्धि योजना (SSY) भारतीय…
How to whitelist morpho device How to whitelist morpho device : Morpho Device का उपयोग करने के लिए Device को Whitelist…
How to cancel Jio recharge and get refund? Jio is one of the largest mobile network operators in India, providing…
Amazon Franchise Kaise Le? Duniya bhar mein online shopping ka trend tezi se badh raha hai, aur Amazon jaise e-commerce…
In today's fast-paced world, where convenience and accessibility are paramount, it's no surprise that financial services have also evolved to…